#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define N 30
typedef struct contacts
{ char CONTACTSPhone[30];
char CONTACTSName[10];
char CONTACTSAdress[10];
char CONTACTSPost[30];
} CONTACTS;
void access (CONTACTS con[],int n);
void writetoFile (CONTACTS con[],int i);
int ReadfromFile(CONTACTS con[]);
void printfcontacts(CONTACTS con[],int n);
void SearchinFile(char fileName[] ,long k);
int main()
{ CONTACTS con[N] ;
int x , i , n ,j ,m ;
long k ;
printf(” 1 存取 \n”);
printf(” 2 显示 \n”);
printf(” 3 删除记录 \n”);
printf(” 4 查询记录 \n”);
printf(” 0 退出程序 \n”);
for(i=0;i<100;i++)
{
printf(“输入你需要的功能对应的数字\n”);
scanf (“%d”,&x);
if (x==1)
{ printf(“存入几个联系人?\n”);
scanf (“%d”,&n);
access(con,n);
writetoFile(con,n);
}
if(x==2)
{
m=ReadfromFile(con);
printfcontacts(con,m);
}
if(x==4)
{
printf(“需要查找第几个联系人?”);
scanf(“%ld”,&k);
SearchinFile(“contacts.txt”,k);
}
if(x==0)
{
printf(“谢谢使用”);
break;}
printf(“\n”);}
}
void access (CONTACTS con[],int n)
{ int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{ printf(“输入第%d个联系人姓名\n”,i+1);
scanf(“%s”,con[i].CONTACTSName);
printf(“输入第%d个联系人电话号码\n”,i+1);
scanf(“%s”,con[i].CONTACTSPhone);
printf(“输入第%d个联系人邮编\n”,i+1);
scanf(“%s”,con[i].CONTACTSPost);
printf(“输入第%d个联系人地址\n”,i+1);
scanf(“%s”,con[i].CONTACTSAdress);
}
}
void writetoFile(CONTACTS con[],int n)
{ int i;
FILE *fp;
if((fp=fopen(“contacts.txt”,”w”))==NULL)
{
printf(“打开文件失败!\n”);
exit (0);
} for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{ fprintf (fp, “%4s”, con[i].CONTACTSName);
fprintf (fp, ” %11s”,con[i].CONTACTSPhone);
fprintf (fp, “%19s”,con[i].CONTACTSPost);
fprintf (fp, “%6s\n”, con[i].CONTACTSAdress);}
fclose(fp);
}
int ReadfromFile(CONTACTS con[])
{
FILE *fp;
int i ;
if((fp=fopen(“contacts.txt”,”r”))==NULL)
{
printf(“failure to open the file”);
exit(0);
}
for(i=0;!feof(fp);i++)
{
fscanf(fp, “%4s”, con[i].CONTACTSName);
fscanf(fp, ” %11s”, con[i].CONTACTSPhone);
fscanf(fp, “%19s”, con[i].CONTACTSPost);
fscanf(fp, “%6s”, con[i].CONTACTSAdress);
}
fclose(fp);
return i-1;
}
void printfcontacts(CONTACTS con[],int n)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{ printf (“%4s”, con[i].CONTACTSName);
printf (” %11s”,con[i].CONTACTSPhone);
printf (“%19s”,con[i].CONTACTSPost);
printf (“%6s\n”, con[i].CONTACTSAdress);
}
}
void SearchinFile(char fileName[] ,long k)
{ int i ;
FILE *fp;
CONTACTS con;
if((fp=fopen(fileName,”r”))==NULL)
{
printf(“打开文件失败!\n”);
exit (0);
}
fseek(fp,(k-1)*sizeof(CONTACTS),SEEK_SET);
fread(&con,sizeof(CONTACTS), 1,fp);
printf (“%4s”, con.CONTACTSName);
printf (” %11s”,con.CONTACTSPhone);
printf (“%19s”,con.CONTACTSPost);
printf (“%6s\n”, con.CONTACTSAdress);
fclose(fp);
}
这是 程序 主要问题 出现在第四个功能
这是运行结果: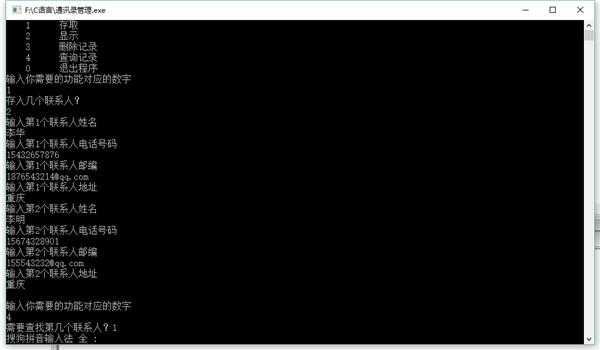
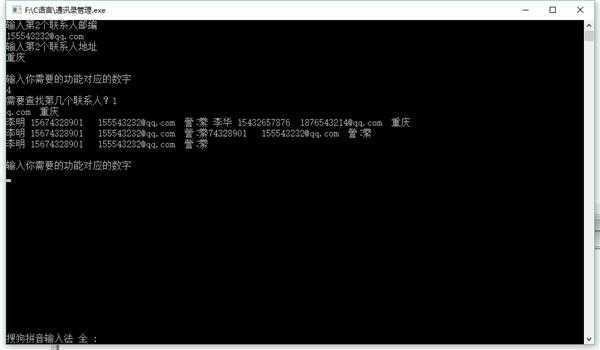
这是记事本存储的:
李华 15432657876 1876543214@qq.com 重庆
李明 15674328901 155543232@qq.com 重庆
#include <stdlib.h>
#define N 30
typedef struct contacts
{ char CONTACTSPhone[30];
char CONTACTSName[10];
char CONTACTSAdress[10];
char CONTACTSPost[30];
} CONTACTS;
void access (CONTACTS con[],int n);
void writetoFile (CONTACTS con[],int i);
int ReadfromFile(CONTACTS con[]);
void printfcontacts(CONTACTS con[],int n);
void SearchinFile(char fileName[] ,long k);
int main()
{ CONTACTS con[N] ;
int x , i , n ,j ,m ;
long k ;
printf(” 1 存取 \n”);
printf(” 2 显示 \n”);
printf(” 3 删除记录 \n”);
printf(” 4 查询记录 \n”);
printf(” 0 退出程序 \n”);
for(i=0;i<100;i++)
{
printf(“输入你需要的功能对应的数字\n”);
scanf (“%d”,&x);
if (x==1)
{ printf(“存入几个联系人?\n”);
scanf (“%d”,&n);
access(con,n);
writetoFile(con,n);
}
if(x==2)
{
m=ReadfromFile(con);
printfcontacts(con,m);
}
if(x==4)
{
printf(“需要查找第几个联系人?”);
scanf(“%ld”,&k);
SearchinFile(“contacts.txt”,k);
}
if(x==0)
{
printf(“谢谢使用”);
break;}
printf(“\n”);}
}
void access (CONTACTS con[],int n)
{ int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{ printf(“输入第%d个联系人姓名\n”,i+1);
scanf(“%s”,con[i].CONTACTSName);
printf(“输入第%d个联系人电话号码\n”,i+1);
scanf(“%s”,con[i].CONTACTSPhone);
printf(“输入第%d个联系人邮编\n”,i+1);
scanf(“%s”,con[i].CONTACTSPost);
printf(“输入第%d个联系人地址\n”,i+1);
scanf(“%s”,con[i].CONTACTSAdress);
}
}
void writetoFile(CONTACTS con[],int n)
{ int i;
FILE *fp;
if((fp=fopen(“contacts.txt”,”w”))==NULL)
{
printf(“打开文件失败!\n”);
exit (0);
} for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{ fprintf (fp, “%4s”, con[i].CONTACTSName);
fprintf (fp, ” %11s”,con[i].CONTACTSPhone);
fprintf (fp, “%19s”,con[i].CONTACTSPost);
fprintf (fp, “%6s\n”, con[i].CONTACTSAdress);}
fclose(fp);
}
int ReadfromFile(CONTACTS con[])
{
FILE *fp;
int i ;
if((fp=fopen(“contacts.txt”,”r”))==NULL)
{
printf(“failure to open the file”);
exit(0);
}
for(i=0;!feof(fp);i++)
{
fscanf(fp, “%4s”, con[i].CONTACTSName);
fscanf(fp, ” %11s”, con[i].CONTACTSPhone);
fscanf(fp, “%19s”, con[i].CONTACTSPost);
fscanf(fp, “%6s”, con[i].CONTACTSAdress);
}
fclose(fp);
return i-1;
}
void printfcontacts(CONTACTS con[],int n)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{ printf (“%4s”, con[i].CONTACTSName);
printf (” %11s”,con[i].CONTACTSPhone);
printf (“%19s”,con[i].CONTACTSPost);
printf (“%6s\n”, con[i].CONTACTSAdress);
}
}
void SearchinFile(char fileName[] ,long k)
{ int i ;
FILE *fp;
CONTACTS con;
if((fp=fopen(fileName,”r”))==NULL)
{
printf(“打开文件失败!\n”);
exit (0);
}
fseek(fp,(k-1)*sizeof(CONTACTS),SEEK_SET);
fread(&con,sizeof(CONTACTS), 1,fp);
printf (“%4s”, con.CONTACTSName);
printf (” %11s”,con.CONTACTSPhone);
printf (“%19s”,con.CONTACTSPost);
printf (“%6s\n”, con.CONTACTSAdress);
fclose(fp);
}
这是 程序 主要问题 出现在第四个功能
这是运行结果:


这是记事本存储的:
李华 15432657876 1876543214@qq.com 重庆
李明 15674328901 155543232@qq.com 重庆
解决方案
10
其实不是乱码问题,而是你的程序设计的文件,你使用结构体来存储信息,但是写入的时候又不是写入的结构体。
40
乱码是原因是你存的时候一行只有41个字符,加上最后的换行符(假如是windows下那么一共就是43个字符)
而你fread的时候直接就是读取sizeof(contacts)那么长的长度自然乱码了
本人没有修改你存文件的地方,只是在SearchinFile函数里改了,有三处:
1.memset(&con, 0, sizeof(CONTACTS)); //需要memset一下,原因是你fread的时候是没有\0补进来的
2.fseek(fp,(k-1)*43,SEEK_SET); //4+12+19+6+2=43(最后的+2是换行符,windows下是\r\n)
3.fread(&con.CONTACTSName,4, 1,fp); //每个成员都分别fread
而你fread的时候直接就是读取sizeof(contacts)那么长的长度自然乱码了
本人没有修改你存文件的地方,只是在SearchinFile函数里改了,有三处:
1.memset(&con, 0, sizeof(CONTACTS)); //需要memset一下,原因是你fread的时候是没有\0补进来的
2.fseek(fp,(k-1)*43,SEEK_SET); //4+12+19+6+2=43(最后的+2是换行符,windows下是\r\n)
3.fread(&con.CONTACTSName,4, 1,fp); //每个成员都分别fread
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define N 30
typedef struct contacts
{
char CONTACTSPhone[30];
char CONTACTSName[10];
char CONTACTSAdress[10];
char CONTACTSPost[30];
} CONTACTS;
void access (CONTACTS con[],int n);
void writetoFile (CONTACTS con[],int i);
int ReadfromFile(CONTACTS con[]);
void printfcontacts(CONTACTS con[],int n);
void SearchinFile(char fileName[] ,long k);
int main()
{
CONTACTS con[N] ;
int x , i , n ,j ,m ;
long k ;
printf(" 1 存取 \n");
printf(" 2 显示 \n");
printf(" 3 删除记录 \n");
printf(" 4 查询记录 \n");
printf(" 0 退出程序 \n");
for(i=0;i<100;i++)
{
printf("输入你需要的功能对应的数字\n");
scanf ("%d",&x);
if (x==1)
{ printf("存入几个联系人?\n");
scanf ("%d",&n);
access(con,n);
writetoFile(con,n);
}
if(x==2)
{
m=ReadfromFile(con);
printfcontacts(con,m);
}
if(x==4)
{
printf("需要查找第几个联系人?");
scanf("%ld",&k);
SearchinFile("contacts.txt",k);
}
if(x==0)
{
printf("谢谢使用");
break;}
printf("\n");}
}
void access (CONTACTS con[],int n)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("输入第%d个联系人姓名\n",i+1);
scanf("%s",con[i].CONTACTSName);
printf("输入第%d个联系人电话号码\n",i+1);
scanf("%s",con[i].CONTACTSPhone);
printf("输入第%d个联系人邮编\n",i+1);
scanf("%s",con[i].CONTACTSPost);
printf("输入第%d个联系人地址\n",i+1);
scanf("%s",con[i].CONTACTSAdress);
}
}
void writetoFile(CONTACTS con[],int n)
{
int i;
FILE *fp;
if((fp=fopen("contacts.txt","w"))==NULL)
{
printf("打开文件失败!\n");
exit (0);
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
fprintf (fp, "%4s", con[i].CONTACTSName);
fprintf (fp, " %11s",con[i].CONTACTSPhone);
fprintf (fp, "%19s",con[i].CONTACTSPost);
fprintf (fp, "%6s\n", con[i].CONTACTSAdress);
}
fclose(fp);
}
int ReadfromFile(CONTACTS con[])
{
FILE *fp;
int i ;
if((fp=fopen("contacts.txt","r"))==NULL)
{
printf("failure to open the file");
exit(0);
}
for(i=0;!feof(fp);i++)
{
fscanf(fp, "%4s", con[i].CONTACTSName);
fscanf(fp, " %11s", con[i].CONTACTSPhone);
fscanf(fp, "%19s", con[i].CONTACTSPost);
fscanf(fp, "%6s", con[i].CONTACTSAdress);
}
fclose(fp);
return i-1;
}
void printfcontacts(CONTACTS con[],int n)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf ("%4s", con[i].CONTACTSName);
printf (" %11s",con[i].CONTACTSPhone);
printf ("%19s",con[i].CONTACTSPost);
printf ("%6s\n", con[i].CONTACTSAdress);
}
}
void SearchinFile(char fileName[] ,long k)
{
int i ;
FILE *fp;
CONTACTS con;
memset(&con, 0, sizeof(CONTACTS));
if((fp=fopen(fileName,"r"))==NULL)
{
printf("打开文件失败!\n");
exit (0);
}
//fseek(fp,(k-1)*sizeof(CONTACTS),SEEK_SET);
//fread(&con,sizeof(CONTACTS), 1,fp);
fseek(fp,(k-1)*43,SEEK_SET);
fread(&con.CONTACTSName,4, 1,fp);
printf ("%4s", con.CONTACTSName);
fread(&con.CONTACTSPhone,12, 1,fp);
printf (" %11s",con.CONTACTSPhone);
fread(&con.CONTACTSPost,19, 1,fp);
printf ("%19s",con.CONTACTSPost);
fread(&con.CONTACTSAdress,6, 1,fp);
printf ("%6s\n", con.CONTACTSAdress);
fclose(fp);
}
10
对电脑而言没有乱码,只有二进制字节;对人脑才有乱码。
推荐使用WinHex软件查看硬盘或文件或内存中的原始字节内容。
不要把
fopen(“…”,”…”);fscanf,fprintf,fgets,fgetc,fclose //读时把\r\n替换成\n,写时把\n替换成\r\n;读到\x1a就设置EOF;读写的内容当字符看待
和
fopen(“…”,”…b“);fseek,ftell,fread,fwrite,fgetc,fclose //不作以上替换,遇到\x1a仍继续读;读写的内容当字节看待
弄混了
推荐使用WinHex软件查看硬盘或文件或内存中的原始字节内容。
不要把
fopen(“…”,”…”);fscanf,fprintf,fgets,fgetc,fclose //读时把\r\n替换成\n,写时把\n替换成\r\n;读到\x1a就设置EOF;读写的内容当字符看待
和
fopen(“…”,”…b“);fseek,ftell,fread,fwrite,fgetc,fclose //不作以上替换,遇到\x1a仍继续读;读写的内容当字节看待
弄混了